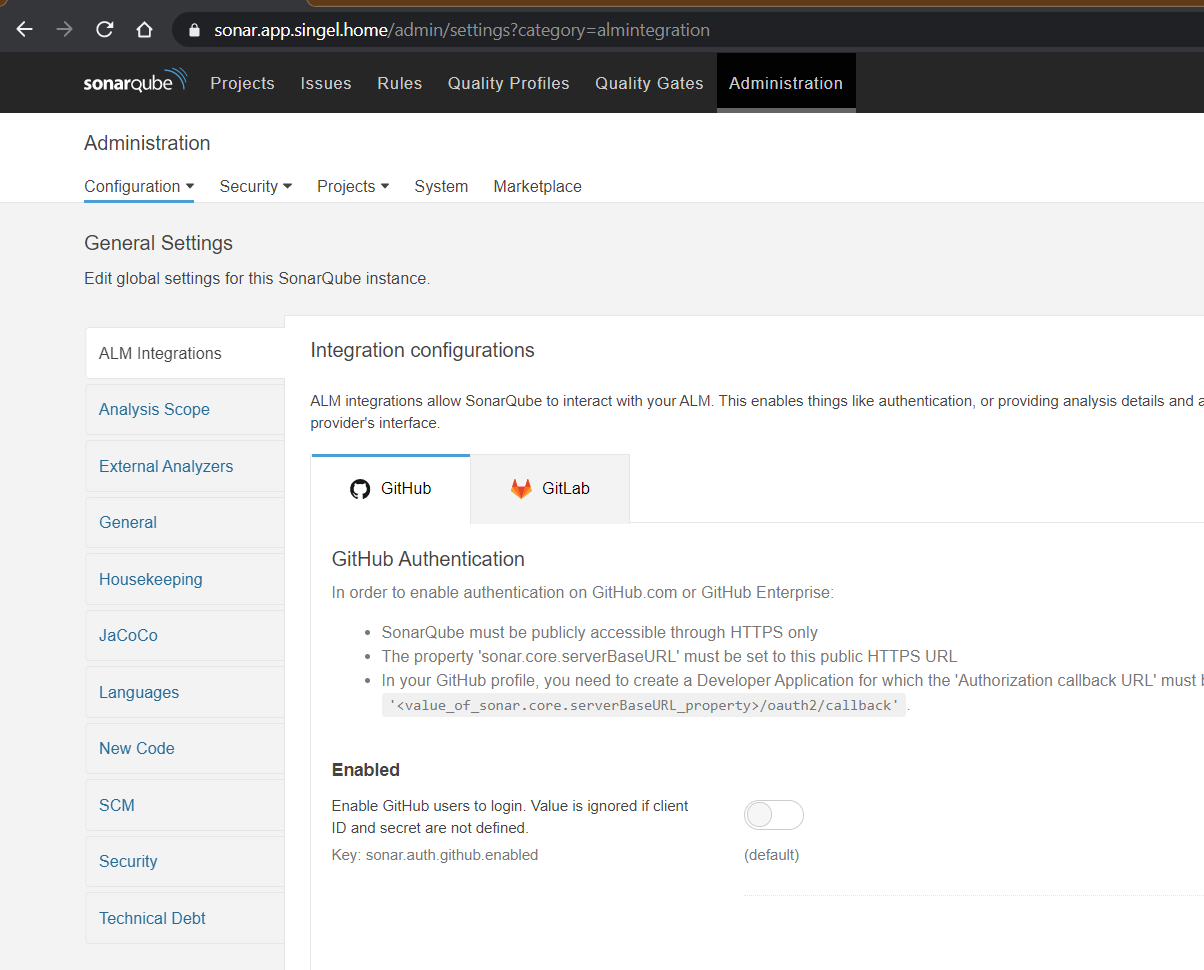
Next up in my migration to K8s is SonarQube. SonarQube needs persistent storage so the first thing to enable is the storage add-on in MicroK8s:
sudo microk8s enable storage
This will give you a Storage Class in K8s. Next thing is to make a deployment for SonarQube that will be using this storage class, by creating a Persistent Volume, a Storage Claim and a Deployment for SonarQube:
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolume
metadata:
name: sonar-data-disk
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
capacity:
storage: 8Gi
hostPath:
path: /data/sonar
storageClassName: microk8s-hostpath
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: sonar-data-disk
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 8Gi
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: sonarqube
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
name: sonarqube
template:
metadata:
name: sonarqube
labels:
name: sonarqube
spec:
nodeName: micro2.singel.home
containers:
- image: sonarqube:latest
name: sonarqube
ports:
- containerPort: 9000
name: sonarqube
volumeMounts:
- name: sonar-data-disk
mountPath: /opt/sonarqube/data
volumes:
- name: sonar-data-disk
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: sonar-data-disk
Note that because we are using hostpath Persistent Storage I've bound this deployment to a specific node with nodeName. This is an issue I will solve in a later post.
I want to use a K8s Ingress for SonarQube because then I will be able to do SSL offloading in there, and I also want this ingress to be loadbalanced. To start off I'll start with enabling those two add-ons to MicroK8s:
sudo microk8s enable ingress
sudo microk8s enable metallb:192.168.1.20-192.168.1.30
To link the two together (the LB to the ingress) you need this:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: lb-ingress
namespace: ingress
spec:
selector:
name: nginx-ingress-microk8s
type: LoadBalancer
ports:
- name: http
protocol: TCP
port: 80
targetPort: 80
- name: https
protocol: TCP
port: 443
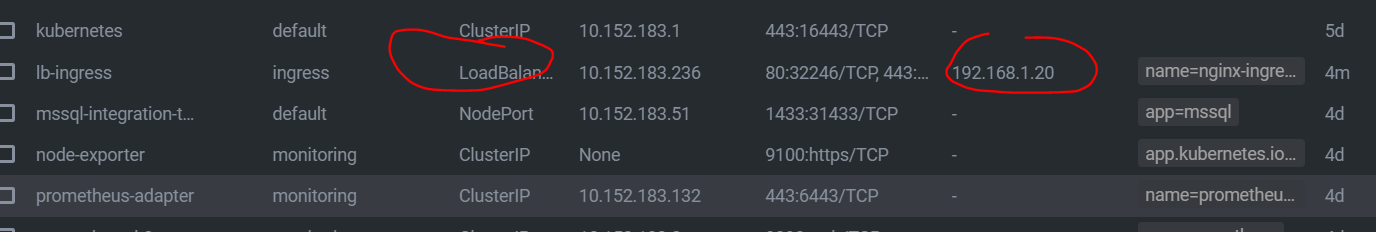
targetPort: 443This should create a loadbalancer IP in the range you gave it when enabling it. In my case 192.168.1.20:
Now if you browse it this IP, it should show you the nginx 404 page:
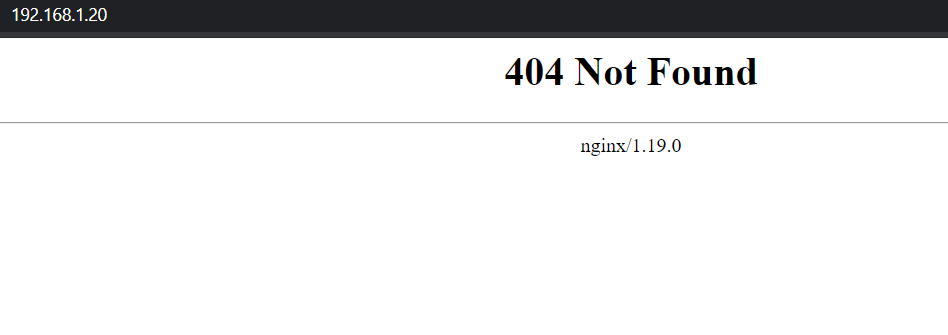
This is because we still haven't setup our ingress rule. Let's take care of that. First we need to expose the SonarQube application with a ClusterIP Service:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: sonar-service
spec:
selector:
name: sonarqube
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 9000
targetPort: 9000Now we can bind our Ingress rule to this service like this:
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: ingress-test
spec:
rules:
- host: "sonar.app.singel.home"
http:
paths:
- pathType: Prefix
path: "/"
backend:
service:
name: sonar-service
port:
number: 9000We should have a working SonarQube at this point, when browsing to the hostname (make sure this dns name resolves first, to the Loadbalancer IP):
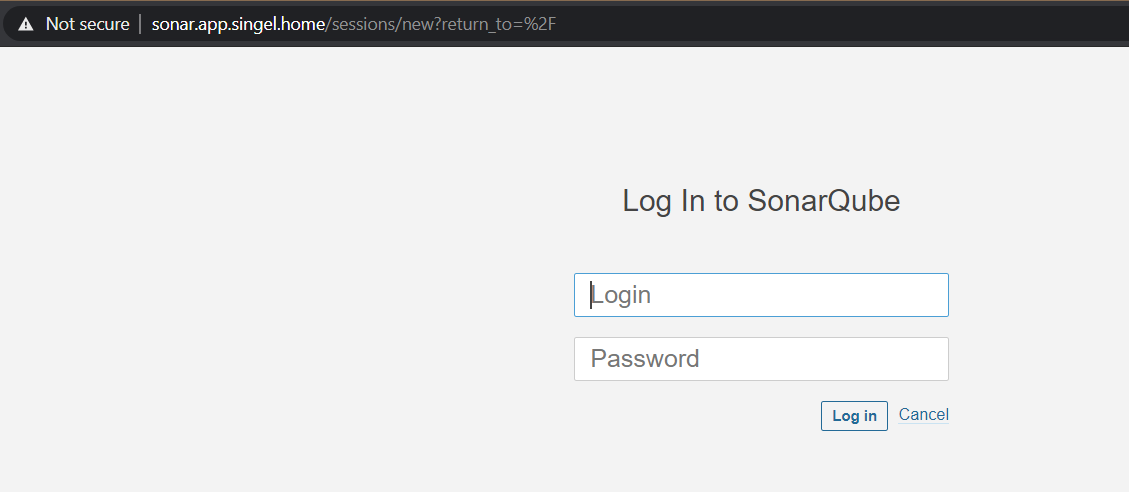
This leaves us with only one thing to fix, and that is the certificate used by the ingress service. I will use a self-signed wildcard certificate for that:
openssl req -x509 -newkey rsa:4096 -sha256 -days 3650 -nodes -keyout key.cer -out cert.cer -subj "/CN=.app.singel.home" -addext "subjectAltName=DNS:.app.singel.home"
And import this as a secret into K8s:
kubectl create secret tls ingress-cert --key key.cer --cert cert.cer
Now there are several ways to make the ingress point to this certificate, but in MicroK8s by far the easiest is to disable and re-enable the ingress add-on:
sudo microk8s disable ingress
sudo microk8s enable ingress:default-ssl-certificate=default/ingress-cert
And presto, SonarQube is available on https on K8s: